Introduction to federated services
Helix Core Server Administrator Guide: Fundamentals explains how you create, configure, and maintain a single Helix Core Server. Small organizations often find a single server is adequate to meet user needs. However, as the business grows and usage expands in scale and geography, many organizations deploy a more powerful server-side infrastructure.
| Architecture | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Tip
|
|
|
Tip
Can display a friendly "Down for Maintenance" message when the p4d process is offline for maintenance or failover (as opposed to a TCP connect error)
|
|
|
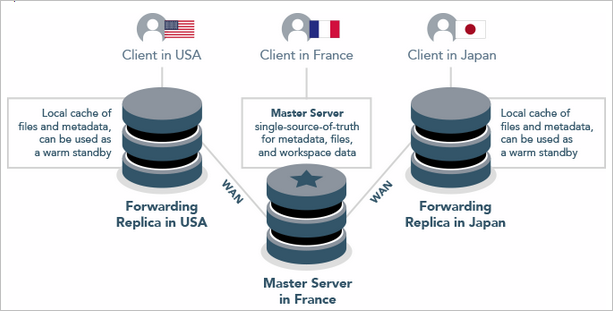
Forwarding replica
|
|
Tip
Starting with 2018.2, we recommend a standby server with rpl.journalcopy.location=1 for high availability and disaster recovery. |
|
|
|
|
For a more detailed summary of replica server types, see the Support Knowledgebase article, "Replica Types and Use Cases".
Other types of federated architecture
A federated architecture might also include servers dedicated to centralized authorization and changelist numbering. See Configuring centralized authorization and changelist servers.