Blog
September 30, 2025
5 Essential IP Governance Processes to Ensure Semiconductor Quality
Embedded Systems & Chip Design
Today’s high-pressure semiconductor design teams need to manage thousands or even millions of IP (intellectual property) blocks across global teams while ensuring complex design architecture meets all verification steps. With chip tapeout success rates at an all-time low of 14%, attention to IP governance and quality should be top-of-mind. Without the proper tools and processes in place, you risk costly delays, compliance failures, and reputational damage.
This guide details the five essential processes that form the foundation of a robust IP governance framework:
- IP Need
- IP Request
- IP Lifecycle
- IP Access Request
- IP Bill of Materials
By implementing these core processes and supporting them with a robust IP management tool like Perforce IPLM, you’ll establish the control and visibility you need to move through complex design cycles efficiently and confidently.
Table of Contents
- The Importance of IP Governance
- 5 Core Governance Processes to Ensure IP Quality
- IP Promotion and Demotion: Rules, Automation, and Quality Gates
- How Perforce IPLM Enables Complete IP Governance
- 5 Benefits of Perforce IPLM for Governing Your IP
- 10 IP Governance Best Practices for Semiconductor Teams
- Build Your IP Governance Framework with Perforce IPLM
The Importance of IP Governance
IP governance is the systematic framework of rules, policies, and enforcement mechanisms used to manage intellectual property assets across their entire lifecycle. Its goal is to ensure that every IP block—whether developed internally, acquired from a third party, or open-sourced—meets stringent quality, security, and compliance standards. Unfortunately, a single flawed IP can compromise the functionality of an entire System on a Chip (SoC) and send design cycles back to square one.
Poor IP management leads to integration problems, verification failures, and security vulnerabilities. Conversely, robust IP governance processes create a predictable and reliable design environment that drives project success. They establish clear accountability, streamline collaboration, and reduce the risk of human error, resulting in higher-quality silicon and faster time-to-market.
Back to top5 Core Governance Processes to Ensure IP Quality
Effective IP governance is built upon five interconnected processes. By following best practices at each stage—from concept to tapeout—you’ll ensure that your final design uses the correct IP at the appropriate maturity level.
1. IP Need: Requirement Tracking and Planning
Before any IP is sourced or developed, its functional and non-functional requirements must be clearly defined, documented, and validated. IP Need achieves this by establishing a formal system that tracks all IP requirements. This upfront planning prevents downstream issues that become more costly later in the cycle.
Best practices for the IP Need process include:
- Early Requirement Identification: Document all technical specifications, performance targets, power constraints, and compliance standards at the project's outset.
- Aligning IP with Project Needs: Ensure each IP block directly supports the overall project goals and integrates appropriately with the design architecture.
- Stakeholder Buy-In: Ensure all relevant teams, from architecture to verification and software, agree on the requirements.
- Comprehensive Tracking: Use dedicated systems to track the status of each IP’s requirements, dependencies, and any changes throughout the project.
By establishing a solid foundation of well-defined needs, teams can ensure that the selected or developed IP align perfectly with project goals while minimizing the risk of integration challenges.
2. IP Request: Registration, Permissions and Workstations
Once an IP need is identified, the IP Request process provides a formal mechanism for registering new IP assets and managing their development. This involves creating a unique record for the IP, assigning ownership, and allocating the necessary resources, such as development workstations and software licenses.
Key components of this process include:
- Approval Workflows: Establishing multi-stage approval workflows to ensure that all new IP development or acquisition is justified and aligned with strategic objectives.
- Permission Management: Defining who can access, modify, and approve the IP at various stages of its development.
- Toolchain Integration: Integrating the IP Request system with existing development environments to automate workstation setup and ensure developers have the tools they need.
By formalizing the IP request and registration process, you establish a clear record of ownership and a complete audit trail from the very beginning of the IP's existence.
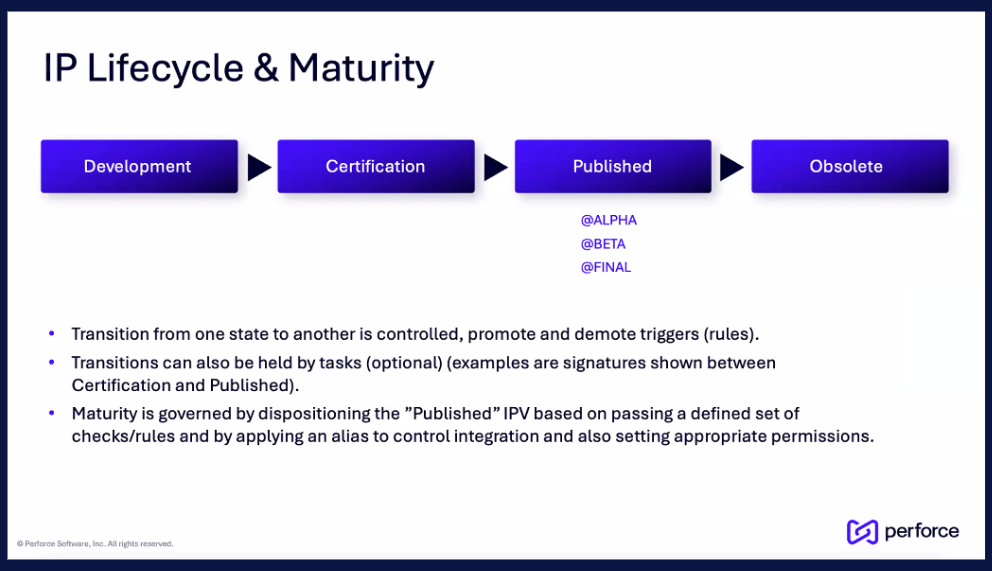
3. IP Lifecycle: Development and Configuration
The IP Lifecycle process creates tailored development cycles for each IP category. For example, a simple, internally developed interface controller has a very different development path than a complex, third-party processor core.
The IP lifecycle follows four primary stages with rules governing how IPs are promoted or demoted through each:
- Development: The initial phase where the IP is created or acquired and undergoes initial verification.
- Certification: The IP is subjected to extensive testing, quality checks, and compliance verification to ensure it meets all requirements.
- Publishing: Once certified, the IP is published to an internal catalog and becomes available for use in design projects.
- Obsolete: When an IP is no longer supported or has been superseded by a newer version, it is marked as obsolete to prevent its use in new designs.
These transitions can trigger automated workflows—such as notifications, audits, or quality gates—to ensure IP quality and reliability.
4. IP Access Request: Licensing and Security Management
With hundreds or thousands of IP blocks in a typical SoC, managing licenses and controlling access presents a formidable challenge. The IP Access Request process establishes a secure system for managing all IP licenses and permissions. This governance reduces the risk of compliance violations and quality issues.
This process involves:
- Permission Frameworks: Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that designers can only access the IP versions they are authorized to use.
- Manage Licenses Effectively: Implement a centralized system to track and manage IP licenses to ensure they comply with licensing agreements and avoid costly violations.
- Automated Workflows: Creating automated workflows for requesting and approving access to specific IP blocks.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining a comprehensive, unalterable record of who accessed which IP, when, and for what purpose.
A robust IP Access Request process protects valuable intellectual property from unauthorized use and makes it easy for designers to find and use the correct, approved versions of each IP.
5. IP Bill of Materials (BoM): Markup, Redlining, and Tapeout Preparation
The final process, the IP Bill of Materials, provides a hierarchical, comprehensive list of every IP block and its specific version used in the SoC design. It serves as the single source of truth for the project's composition.
Key functions of the IP BoM process include:
- Markup and Quality Control: Adding critical markup, such as maturity status, quality metrics, and verification results, to each entry in the BoM.
- Hierarchical Visibility: Structuring the BoM to reflect the design hierarchy and provide complete visibility into all dependencies and sub-dependencies.
- Integration with Verification: Linking the BoM with design verification and validation data to confirm that all IP blocks have passed the necessary quality checks.
A meticulously maintained IP BoM with high-quality IPs is the final confirmation that the design is complete, correct, and ready for tapeout.
Back to topIP Promotion and Demotion: Rules, Automation, and Quality Gates
The movement of IP from one lifecycle stage to the next is governed by a strict, rule-based system that acts as a series of quality gates. For an IP to be promoted to the next stage, it must satisfy all associated rules.
For example, to move from Development to Certification, an IP might need to pass 100% of its verification tests, have complete documentation, and receive sign-off from the quality assurance team. If it fails to meet these requirements, it will be demoted back to the development stage. 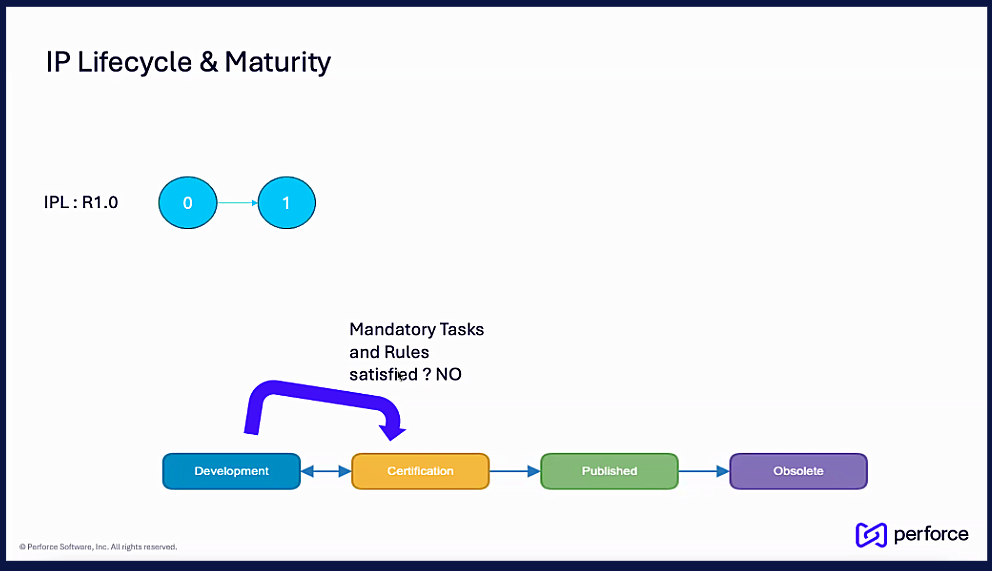
Stage transitions can trigger powerful automations. Once all rules for a promotion are met, an automated workflow can be initiated to update the IP's status, notify relevant stakeholders, and grant new access permissions. Conversely, if an IP fails to meet the required standards, it can be demoted back to a previous stage for remediation. This rule-based system enforces quality at every step of the lifecycle.
Back to topHow Perforce IPLM Enables Complete IP Governance
Modern semiconductor design teams cannot feasibly manage all their IP policies and procedures without a dedicated tool. Perforce IPLM (IP Lifecycle Management) provides a comprehensive foundation for the entire semiconductor design cycle by automating and enforcing the five core governance processes.
Perforce IPLM empowers teams to:
- Track Everything: It creates a single source of truth by tracking all IP versions, design rules, user permissions, metadata, policies, and other critical elements in one centralized platform.
- Navigate All 5 Processes: The platform is purpose-built to manage the entire IP lifecycle, from strategic need planning and request management to lifecycle configuration, access control, and BoM generation.
- Automate and Enforce Rules: With Perforce IPLM, you can import and version-control governance policies. You can create a "route" of tasks for each IP and automate promotions or demotions based on whether the rules are satisfied. As an IP is promoted, a new set of rules and tasks automatically comes into play, ensuring continuous governance.
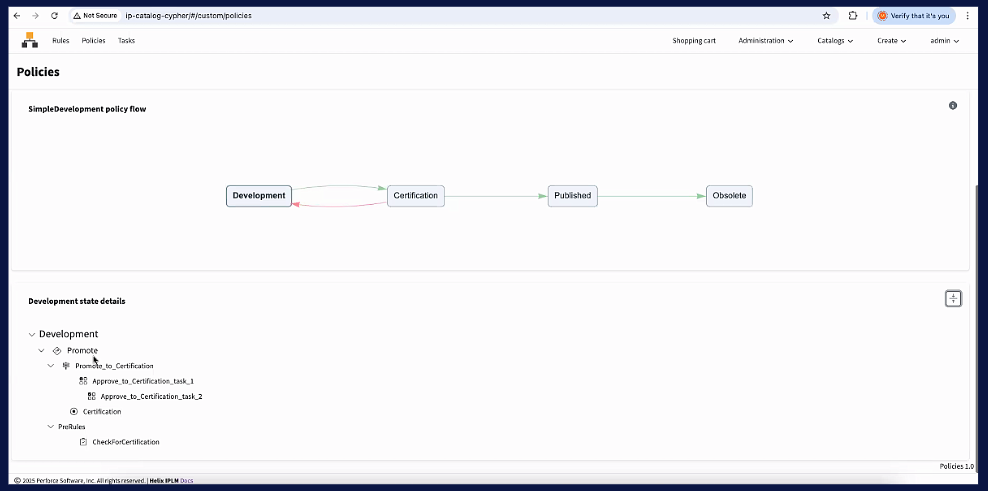
5 Benefits of Perforce IPLM for Governing Your IP
- Traceable IP Ecosystem: Comprehensive search and filtering capabilities give you complete visibility into your entire IP catalog.
- Automated Release Management: Manage hierarchical dependencies so that when an IP is updated, all dependent designs are flagged for review.
- Customizable Dashboards: Get at-a-glance oversight of your governance processes and highlight bottlenecks or compliance issues.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Implement robust, role-based access controls to protect your valuable intellectual property.
- RESTful API: Integrate with your existing toolchain, including EDA tools and requirements management, to create a seamless design environment.
10 IP Governance Best Practices for Semiconductor Teams
Implementing the right IP governance tool is only part of the solution. Following these best practices will create more efficient workflows and reduce the likelihood of errors:
- Establish Clear Policies: Create clear, well-documented governance policies and communicate them across all design and verification teams.
- Implement Role-Based Access: Use role-based access controls (RBAC) and conduct regular permission audits to ensure security.
- Standardize Documentation: Use standardized templates and naming conventions across all IP assets and documentation.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: Establish regular review cycles for both your IP assets and your governance procedures to drive continuous improvement.
- Integrate Governance Checkpoints: Build governance checks directly into your existing design verification workflows.
- Maintain Audit Trails: Ensure comprehensive audit trails are established and automated for compliance, troubleshooting, and process analysis.
- Train Your Teams: Provide thorough training for all team members on governance procedures and the tools used to enforce them.
- Automate Notifications: Implement automated alerts for critical events, such as access denials or promotion failures.
- Measure Effectiveness: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your governance program.
- Monitor Compliance: Regularly check adherence to policies and regulations to avoid potential risks.
Build Your IP Governance Framework with Perforce IPLM
Perforce IPLM provides a comprehensive platform to implement and manage a complete IP governance framework across your entire semiconductor design lifecycle.
From planning and development to certification and tapeout, you’ll enforce policies, streamline workflows, and ensure every IP meets the necessary standards for quality and compliance.
Connect with an IPLM expert to learn how Perforce IPLM can help your team streamline complexity and ensure quality through comprehensive IP governance.
Watch a free demo of Perforce IPLM now.