Blog
May 14, 2025
Automotive Industry Trends 2025: AI in Automotive Software Development
AI,
Security & Compliance
Since the first vehicles were sold to customers, automakers have competed to deliver the newest features and the greatest benefits to the driving experience. Today, that competition is less about shaping a car’s physical characteristics and more about making cars smarter and more connected to the world around them.
With thousands of car models and trim levels available worldwide, there is a fierce need to find new ways to stand out from the competition. Fueled by consumers’ increasing demands for internet connectivity, interactive dashboards, and autonomous driving, manufacturers rely heavily on software, with AI playing a central role in how they design, build, and update vehicles.
Automotive AI is not without its challenges. As global regulators and consumers scrutinize AI applications, manufacturers must develop new strategies to ensure safe and scalable innovation.
This blog takes data from our 2025 State of Automotive Software Development report to help you understand the evolving role of AI in automotive software development, the challenges manufacturers face, and how static analysis helps maintain safe, secure, and reliable code within AI-based systems.
Read along or jump ahead to the section that interests you most:
Get Your Copy: 2025 State of Automotive Software Development Report
Back to topGrowth of AI in the Automotive Industry Remains Steady
Our survey of over 650 automotive professionals worldwide provides valuable insights into AI's impact on the industry. The need to provide something new to consumers is particularly relevant to AI's growth, as the top market challenge cited by respondents was maintaining industry competitiveness at 58%, a 28% increase from the previous year.
This concern was most pronounced for Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, at 28% and 25%, respectively.
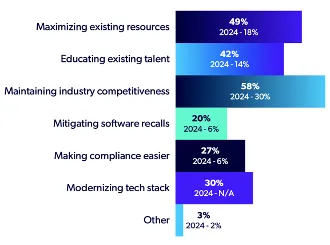
Source: 2025 State of Automotive Software Development Report
The majority of respondents (42%) reported using AI in the design of fully autonomous vehicles. Another 38% said AI is affecting some autonomous components. Year-over-year, that represents a 5% increase in AI use for autonomy. This suggests steady momentum, although it’s unclear whether this focus will shift as technologies and markets evolve.
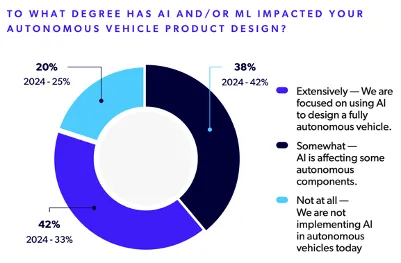
Source: 2025 State of Automotive Software Development Report
Geographically, AI adoption varies. North America, the Middle East, Africa, and Oceania are leading in the use of AI for autonomous design. In Europe, Asia, and Latin America, AI is more often used to support specific components rather than to achieve full vehicle autonomy.
Back to topBenefits of AI in Automotive
AI powers a wide range of features in modern cars, but its most recognizable application is advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). ADAS improves safety and simplifies the driving experience, especially as systems become more autonomous. Typical applications include lane keeping, adaptive cruise control, driver monitoring, and parking assistance.
Examples of how AI supports autonomous functions are global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) and inertial navigation systems (INS) on board vehicles. These components generate massive volumes of sensor data that require AI-based interpretation and real-time decision-making for vehicle movement and control.
AI also transforms how vehicles communicate with the manufacturer. It enables smarter and proactive over-the-air (OTA) updates based on real-time diagnostics and driver behavior. It can also power personalization using algorithms that adjust settings based on driver habits, from seat position to climate control and infotainment preferences.
The use of AI to support vehicle connectivity cannot be understated: 41% of survey respondents stated that AI has somewhat influenced their connectivity features, while 39% reported that it is directly driving connected design decisions.
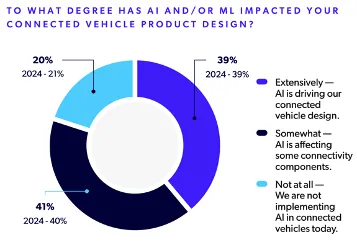
Source: 2025 State of Automotive Software Development Report
Back to topAI's Role in Software Development
The benefits of AI in automotive begin well before vehicles hit the road. In our survey, maximizing existing resources ranked second among the top challenges that manufacturers face, with 49% of respondents identifying it as a priority. As budgets tighten and product complexity increases, many development teams are turning to AI to help achieve more with less, especially as they must demonstrate compliance with standards such as MISRA® and ISO 26262.
Generative AI tools now assist developers with writing, refactoring, testing, and translating code into different languages. These tools generate code from prompts, complete lines, and modernize legacy systems without full rewrites.
The value of generative AI is more nuanced in embedded environments. It can assist in drafting code optimized for resource-constrained systems, such as ADAS platforms. However, its use remains limited due to its unpredictability and black box nature, as explained below.
Generative AI also supports documentation. It can generate API docs, user manuals, and inline code comments. This ensures consistency and maintainability, and reduces onboarding time for new developers.
Back to topConcerns About AI in the Automotive Industry
Despite AI’s potential, automakers must tread carefully. Survey respondents put safety (“Safe decision-making for AI algorithms in autonomous/semi-autonomous vehicles”) and security (“Avoiding vulnerabilities and cyberattacks with the introduction of advanced AI technologies”) as their leading concerns in AI vehicle development.
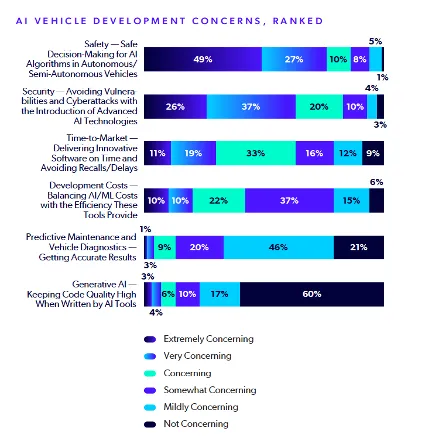
Source: 2025 State of Automotive Software Development Report
📕 Related Resource: How to Comply With ISO 26262 - the Essential Functional Safety Standard for Automotive
AI introduces new challenges to automotive software development as systems must be proven safe before deployment. As Anthony Corso, executive director of the Stanford Center for AI Safety, explains:
“The systems themselves are extremely complex, but the environments we are asking them to operate in are incredibly complex, too. Machine learning has enabled robotic driving in downtown San Francisco, for example, but it’s a huge computational problem that makes validation all the harder.”
These problems include:
- Lack of determinism: Functions such as autonomous driving must respond in predictable, real-time ways. AI models, especially those based on machine learning, may produce different outputs under the same conditions, undermining the predictability required by functional safety standards and testing.
- Limited visibility into code: Standards such as ISO 26262 require full traceability and transparency into development artifacts, while MISRA® compliance necessitates visibility into code. However, many AI components operate as black boxes. This lack of visibility complicates test case generation and validation, especially for components with a high Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL), which require more rigorous procedures.
- Increased exposure to automotive security risks: AI models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where subtle and malicious inputs may cause undesirable behaviors. In safety-critical systems, such manipulation could lead to catastrophic failures, including the introduction of misleading sensor inputs or the bypassing of safety controls.
Interestingly, while code quality remains the top overall concern at 29%, AI-generated code was not a significant concern among the majority of respondents (see figure above). This may reflect a cautious but growing confidence in AI-based tools when applied appropriately.
📕 Related Resource: Automotive Industry Trends 2025 Overview
Back to topHow the Automotive Industry Is Adapting to AI
As AI becomes more embedded in automotive systems, safety standards are evolving. Traditional functional safety frameworks are being reexamined to address AI-specific risks.
One of the newest developments is ISO/DPAS 8800, a standard for AI in road vehicles. It outlines safety measures for AI-driven systems and provides guidance on how to validate their behavior. This is an important step toward ensuring that AI-based components operate within a framework designed for functional safety.
To mitigate risks in the development and compliance of AI-based systems, automotive teams are adopting static analysis tools, like Perforce QAC and Perforce Klocwork, to catch issues earlier in the software lifecycle.
Perforce Static Analysis tools identify defects, vulnerabilities, and compliance issues before they reach testing or deployment. Static analysis acts as an independent safeguard and compliance checker, helping teams to maintain quality and ensure their software meets functional safety requirements.
See for yourself how Perforce static code analyzers accelerate compliance and identify coding errors: Request your free trial today.
Try QAC for code quality and compliance.
QAC Free Trial
Try Klocwork for SAST security at scale.
Back to topFinal Thoughts
The automotive industry is in a software-first era, and AI is changing how developers think and implement new features. From vehicle design to personalized driving experiences and ongoing maintenance, AI is helping teams deliver smarter, safer, and more competitive vehicles.
Based on our survey, manufacturers recognize that AI adoption requires a careful balance between innovation and risk. With the right tools, standards, and strategies, AI presents a powerful path forward for the future of connected and autonomous mobility.
For more automotive software industry insights, download your free copy of this year's report.
▶️ Download Your Copy

