Best Static Code Analyzer for Developer Productivity, SAST, and DevOps
Perforce Klocwork is the preferred static analysis and SAST tool for C, C++, Java, JavaScript, Python, and Kotlin identifies software security, quality, and reliability issues, helping to enforce compliance with standards. Read the Datasheet.
Why Klocwork?
Built for enterprise DevOps and DevSecOps, Klocwork scales to projects of any size, integrates with large complex environments and a wide range of developer tools, and provides control, collaboration, and reporting for the entire enterprise. This has made Klocwork the preferred static code analyzer that keeps development velocity high while enforcing continuous compliance for security and quality.
Perforce Klocwork Key Features
Key Features of Perforce Klocwork
Use Klocwork static application security testing (SAST) for DevOps and DevSecOps. Our security standards identify security vulnerabilities — helping to find and fix security issues early and proving compliance to internationally recognized security standards.
- DevSecOps: Klocwork integrates with CI/CD tools, containers, cloud services, and machine provisioning, making automated security testing easy.
- Security Standards: CWE, OWASP, CERT, PCI DSS, DISA STIG, and ISO/IEC TS 17961.
- Security Vulnerability Detection: SQL Injection, Tainted Data, Buffer Overflow, Vulnerable Coding Practices, and many more.
- Bug, Quality Issue, and Code Smell Detection: Null Pointer Deferences/Exceptions, Memory/Resource Leaks, Uncaught Exceptions, and more.

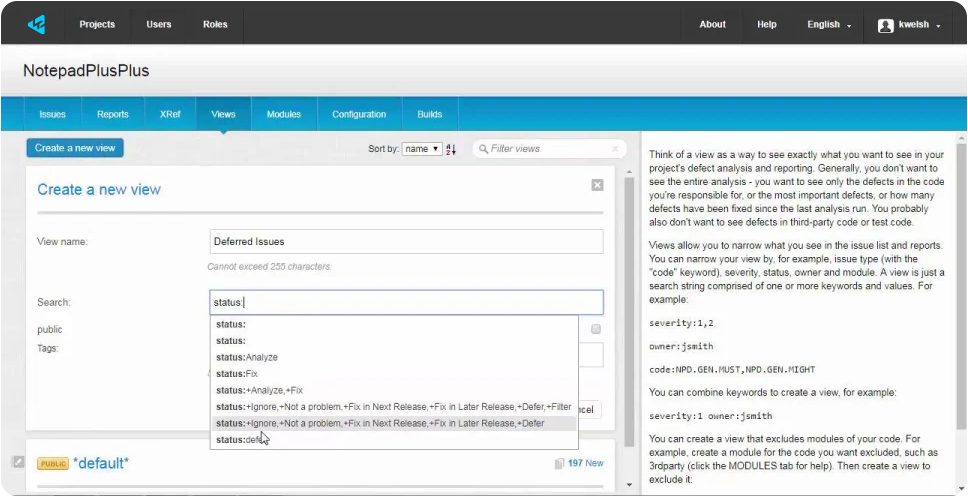
Project Streams provides easy management of shared code bases that have multiple variants or branches by simplifying project rule configuration, issue management, defect citing, reporting, and efficient data storage of analysis data.
Creating streams provides the following benefits:
- Assign a single project rule configuration to all variants.
- Issues common to multiple variants are automatically kept in sync and only require citing once.
- Easily identify identical issues across multiple streams and issues unique to a specific stream.
- Generate reports on individual streams for compliance, functional safety, or other evidential purposes.
- More convenient organization and efficient storage of analysis data.
Perforce Klocwork tools are designed with Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery foremost in our thinking, which makes it easy to include static analysis as part of your CI/CD pipelines.
Using system context data from the Klocwork Server, it is possible to analyze only the files that changed while also providing differential analysis results as if the entire system had been analyzed. This provides you with the shortest possible analysis times.
Klocwork tools have common command line interfaces, the Klocwork defect data can be accessed via a REST API and all output formats use standard formats, such as XML, JSON, and PDF.
Klocwork can be run within containerized and Cloud build systems and supports the provisioning of machine instances as required. Providing maximum flexibility and opportunity to use internal or external Cloud services for code analysis.

Perforce Validate platform is a centralized store of analysis results from Perforce Helix QAC and Perforce Klocwork Static Analysis products. Validate provides analysis data, trends, and configurations for codebases across the organization — accessed through a web browser. It is also highly customizable, enabling your team to easily define specific QA and compliance rule configurations, identify issues and deviations, and review the entirety of the code by project and section to adequately meet your team’s needs.
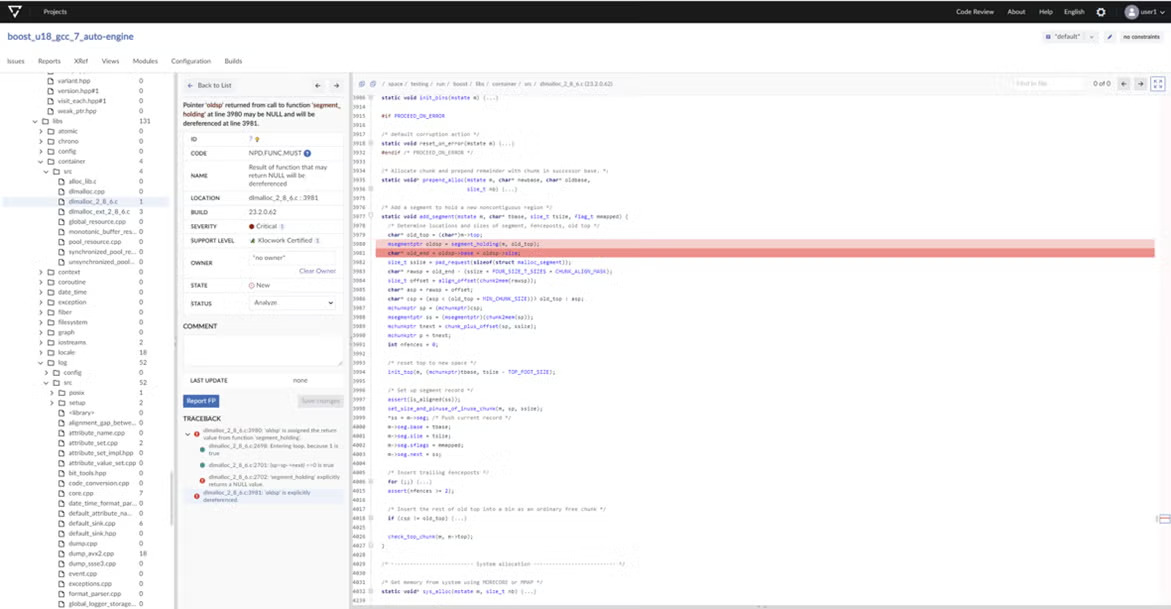
By seamlessly integrating static analysis with the rest of your development toolset, Klocwork will shift-left defect detection and improve developer adoption as a tool for developer training and increasing productivity.
Klocwork provides out of the box support for hundreds of compilers and cross-compilers, so build integration is automatic.
Plugins for popular IDEs (including Microsoft Visual Studio, Eclipse, IntelliJ, and more).
Local code changes made using the connected desktop plugins provide immediate differential analysis results within IDEs.
Intraprocedural defects and coding violations are identified by severity of risk. For each defect and coding violation, you will receive detailed information of cause with rich, context-sensitive help and guidance on remediation. This allows for easily accessible opportunities for understanding and learning.
In addition, Klocwork features a Secure Code Warrior integration, which provides you with software security lessons and training tools for many common development languages as you write code.
A graphical custom checker creation tool makes the implementation of project- or organization-specific rules quick and easy — further enriching the learning opportunities.
Klocwork also integrates with architectural visualization and enforcement tools like Structure 101 to allow users to further improve the overall quality and maintainability of their code base through clean and correct dependencies.
Achieve Coding Standards Compliance
Klocwork makes it easy to comply with coding standards. You can use the following compliance taxonomies to enforce coding standards across your codebase. And, you’ll get fewer false positives and false negatives in your diagnostics.
| Security | C | C++ | C# | Java | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secure coding standards help to safeguard your code from potential cyberthreats and other coding vulnerabilities. (Note: The complete set of security standards may not be available with older versions of Klocwork.) | CERT | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| CWE | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| CWE Top 25 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| OWASP | ✔ | ||||
| DISA STIG | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| PCI DSS | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| ISO/IEC TS 17961 (C secure) | ✔ |
| Safety | C | C++ | C# | Java | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safety standards help to ensure that the software powered by your code is reliable and functionally safe. (Note: The complete set of safety standards may not be available with older versions of Klocwork.) | MISRA C 2004 | ✔ | |||
| MISRA C 2012 | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| MISRA C 2023 | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| HKMC | ✔ | ||||
| MISRA C++ 2008 | ✔ | ||||
| AUTOSAR C++ 14 | ✔ | ||||
| JSF AV C++ | ✔ |
| Quality | C | C++ | C# | Java | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality standards help to ensure that your code is reliable and free of errors. (Note: The complete set of quality standards may not be available with older versions of Klocwork.) | NASA's 10 Rules | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Klocwork Quality | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Customize | C | C++ | C# | Java | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| You can create and customize your own rules or project/business coding standard for C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, and Python. | Create Your Own Standard | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Create Your Own Rules | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
“With Perforce Klocwork, our productivity has dramatically increased, leaving us with more time to mitigate potential problems leveraging the ‘what if’ testing. As a result, our end product is stronger, and Raytheon can get the end product to our customers more quickly than before.”

Certified for ISO, IEC, and EN Compliance
Perforce Klocwork is independently certified for compliance.
TÜV-SÜD Certified
Perforce Klocwork is TÜV-SÜD certified for compliance with key functional safety standards:
- ISO 26262 (automotive) up to ASIL level D.
- IEC 61508 (general industry) up to SIL 4.
- EN 50716 (railways) up to SW-SIL 4.
- IEC 62304 (medical devices) up to Software Safety Class C.
ISO 9001 Certified
Perforce Klocwork is also certified in ISO 9001.
ISO 9001 is one of the most widely adopted standards. It ensures that organizations are striving to meet and exceed customers’ requirements and satisfaction through continuous improvement.
ISO 27001 Certified
Perforce Klocwork is also certified in ISO 27001.
ISO 27001 gives specific requirements that an organization must meet in order to be certified by an accredited certification body following the successful completion of an audit.
Klocwork Professional Services: Onboarding Packages
When you purchase Klocwork, we bundle in an onboarding package to ensure a successful experience.
Learn More
Try Perforce Klocwork
Request your free trial of Perforce Klocwork for C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, and Kotlin.
See Klocwork Live
Start with your custom demo, or access our on‑demand Klocwork demo to get an immediate look Klocwork's features.